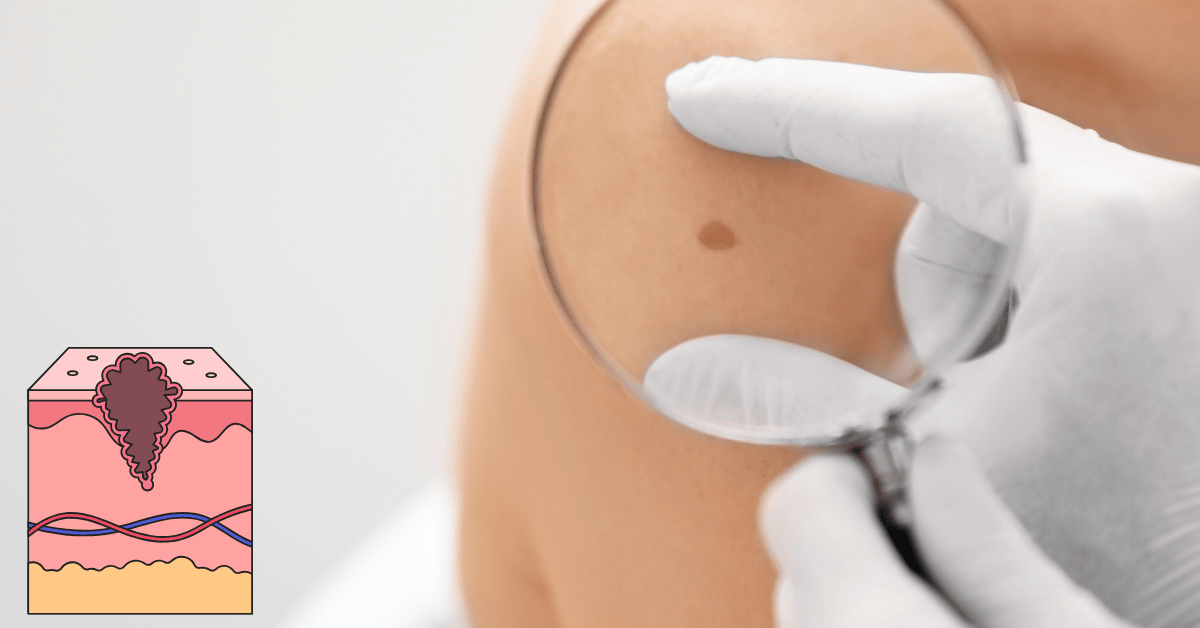
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of skin cells. This abnormal growth often occurs when the DNA within skin cells becomes damaged, usually due to environmental factors like ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
As these damaged cells proliferate, they can form tumors, leading to various types of skin cancer. Skin cancer is among the most widespread cancers worldwide, impacting millions of people every year. While it can be serious, especially if not detected early, many skin cancers are treatable, particularly in their initial stages.
Types of Skin Cancer
There are three primary types of skin cancer, each originating from different skin cell types and presenting unique characteristics. The most common is Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC), which arises from the basal cells located in the outer layer of the skin.
BCC usually appears as a small, shiny bump or a flat, scaly patch, and it primarily develops in areas frequently exposed to sunlight, such as the face and neck. Fortunately, BCC is typically slow-growing and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, making it highly treatable when caught early.
The second type, Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), originates in the squamous cells, which are flat cells found in the outer layer of the skin. SCC may present as a firm, red nodule or a scaly, crusted lesion. While it can occur in sun-exposed areas, it can also develop in regions not commonly exposed to UV light.
SCC tends to be more aggressive than BCC and has a higher potential to metastasize if left untreated, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
The most serious type is Melanoma, which develops from melanocytes—the pigment-producing cells responsible for skin color. Melanoma can appear as a new mole or changes in an existing one, often characterized by irregular borders, multiple colors, and asymmetry.
Unlike BCC and SCC, melanoma can spread rapidly to other parts of the body, making early detection crucial for successful treatment. Factors such as family history and previous atypical moles can increase the risk of developing melanoma, underscoring the importance of regular skin checks.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of skin cancer, with UV radiation being the leading cause. Prolonged exposure to the sun’s rays, particularly during childhood, can significantly increase the risk. This exposure can cause damage to the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that result in cancerous growth.
Additionally, individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to UV damage and, consequently, skin cancer.
Family history also plays a critical role; having a close relative with skin cancer increases one’s risk due to genetic predispositions. Furthermore, age is a significant factor, as the risk of skin cancer generally increases with age due to cumulative sun exposure over time.
People with weakened immune systems—such as those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy after an organ transplant or those with certain autoimmune diseases—are at a heightened risk for developing skin cancer.
Lastly, a previous history of skin cancer is an important risk factor, as individuals who have had skin cancer once are more likely to develop it again. By understanding these causes and risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their skin and monitor for potential signs of skin cancer.
Common Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of skin cancer early can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Skin cancer can manifest in various ways, and understanding these symptoms is vital for maintaining skin health.
Itchy Skin and Skin Cancer
Itchy skin is a symptom that can sometimes indicate the presence of skin cancer, although it is more commonly linked to benign skin conditions. When the itchiness is persistent and localized—particularly around a suspicious mole or lesion—it may warrant further investigation.
Unlike typical itchiness associated with dryness or irritation, the type linked to skin cancer often does not resolve with over-the-counter treatments.
If you experience persistent itching, it’s essential to consider whether it is accompanied by other changes in the skin. For example, alterations in color, shape, or size of a mole can be significant warning signs.
Additionally, if the itchy area is also bleeding, oozing, or developing a crust, these symptoms should be taken seriously. Such signs could indicate the presence of skin cancer, making it crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Other Signs to Look For
In addition to itchy skin, several other symptoms may suggest skin cancer. Changes in existing moles are particularly important to monitor. Key characteristics to watch for include asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, or a diameter larger than that of a pencil eraser. New growths on the skin, especially if they appear suddenly or change rapidly, can also be potential warning signs of skin cancer.
Moles or lesions that bleed, ooze, or crust over should not be ignored. Furthermore, any sores that do not heal within a few weeks can be concerning. If you notice any combination of these symptoms, it is important to seek an evaluation by a healthcare professional. Detecting skin cancer early can result in more successful treatment and improved results.
Differences Between Skin Cancer and Other Skin Conditions
Differentiating skin cancer from other skin conditions is crucial, as many share similar symptoms. For instance, conditions like eczema and psoriasis often result in itchy, red, and flaky patches, but they typically respond well to topical treatments and do not manifest as suspicious moles or lesions.
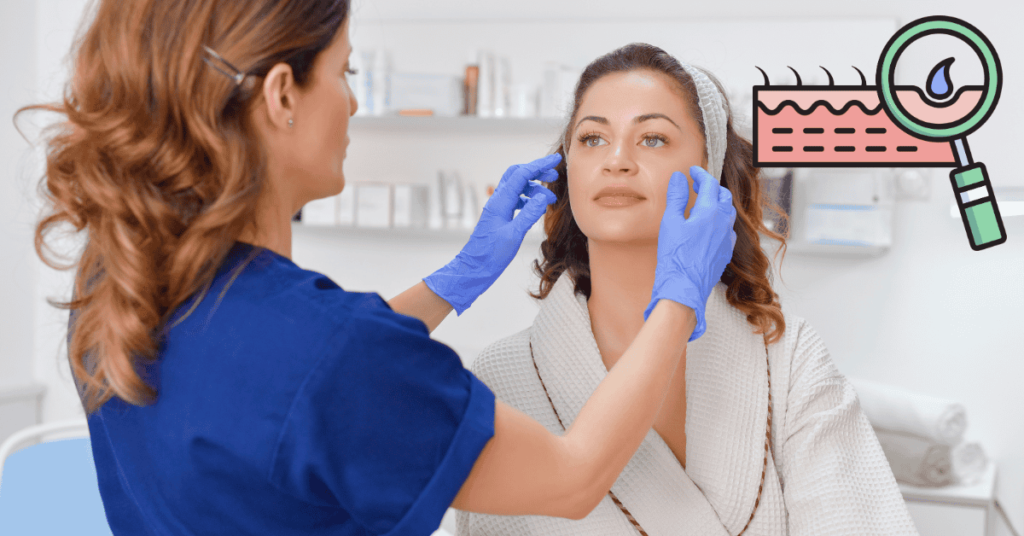

In contrast, benign moles can be itchy but generally exhibit uniform color and consistent shape; any sudden changes in these characteristics should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider.
Skin infections may also cause redness, swelling, and pain, usually accompanied by additional signs of infection, such as fever or pus. Given the variety of skin conditions that can present similarly, it’s essential to err on the side of caution.
If you have any uncertainty about changes in your skin, consulting a healthcare professional is always the best course of action. Early detection and diagnosis of skin cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes, making it essential to stay vigilant about any unusual changes in your skin.
Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing skin cancer and detecting it early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Awareness of the risks and taking proactive measures is crucial for maintaining skin health.
Regular Skin Checks
Conducting regular skin checks is one of the most effective ways to detect skin cancer early. This practice involves examining your skin monthly for any new moles or changes to existing ones. When performing a skin check, look for any asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, or sizes larger than a pencil eraser. Pay particular attention to areas that are often exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, arms, and back.
In addition to self-exams, it’s essential to schedule regular appointments with a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or other risk factors. A dermatologist can perform a thorough skin examination and provide professional advice on skin health. Early detection through regular skin checks can lead to prompt treatment, which is critical for successful outcomes.
Sunscreen and Skin Protection
Sunscreen plays a vital role in skin cancer prevention. Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can help protect your skin from harmful UV radiation, which is a significant risk factor for skin cancer. It’s important to apply sunscreen generously and reapply every two hours, especially if you’re swimming or sweating.
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long sleeves, can further shield your skin from the sun’s rays. Seeking shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) and avoiding tanning beds can also significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. Incorporating these sun protection measures into your daily routine can greatly enhance your skin’s health and longevity.
Conclusion
In summary, being aware of the common symptoms of skin cancer—such as changes in moles, persistent itching, and new growths—is crucial for early detection. Regular skin checks and consultations with a healthcare professional can help identify potential issues before they develop into more serious conditions. Additionally, preventive measures like using sunscreen and practicing sun safety can significantly lower the risk of skin cancer.
Early detection and prevention are key to successfully managing skin cancer, making it essential to stay vigilant and proactive about skin health. By understanding the symptoms and taking preventive actions, individuals can significantly enhance their chances of early diagnosis and successful treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the common symptoms of skin cancer?
Common symptoms include changes in moles, persistent itching, new growths, and sores that do not heal.
How often should I perform self-skin checks?
It is recommended to conduct self-skin checks at least once a month.
What type of sunscreen should I use?
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and reapply every two hours.
Can skin cancer be cured?
Yes, skin cancer can often be cured if detected early, but treatment varies based on the type and stage.
Who is at higher risk for skin cancer?
Individuals with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer are at higher risk.
What should I do if I notice changes in my skin?
If you notice any unusual changes, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.