What Are Scaly Patches?
Definition and Characteristics
Scaly patches are defined as areas of skin that exhibit dryness and flakiness, often leading to a rough texture. These patches can vary significantly in appearance, including differences in color—ranging from white or gray to reddish or brown shades. The texture can also differ, with some patches appearing raised while others lie flat against the skin.
These patches typically indicate a disruption in the skin’s natural barrier, which can result from a variety of factors, including environmental conditions, allergies, or underlying skin disorders.
Scaly patches may be accompanied by other symptoms such as itching, irritation, or inflammation, which can vary in intensity. It’s important to note that the presence of scaly patches may signal an underlying condition that could require medical attention.
Common Locations on the Body
Scaly patches can develop on almost any part of the body, but certain areas are more prone to these skin changes due to the skin’s structure and exposure to irritants. Here are some of the most common locations:
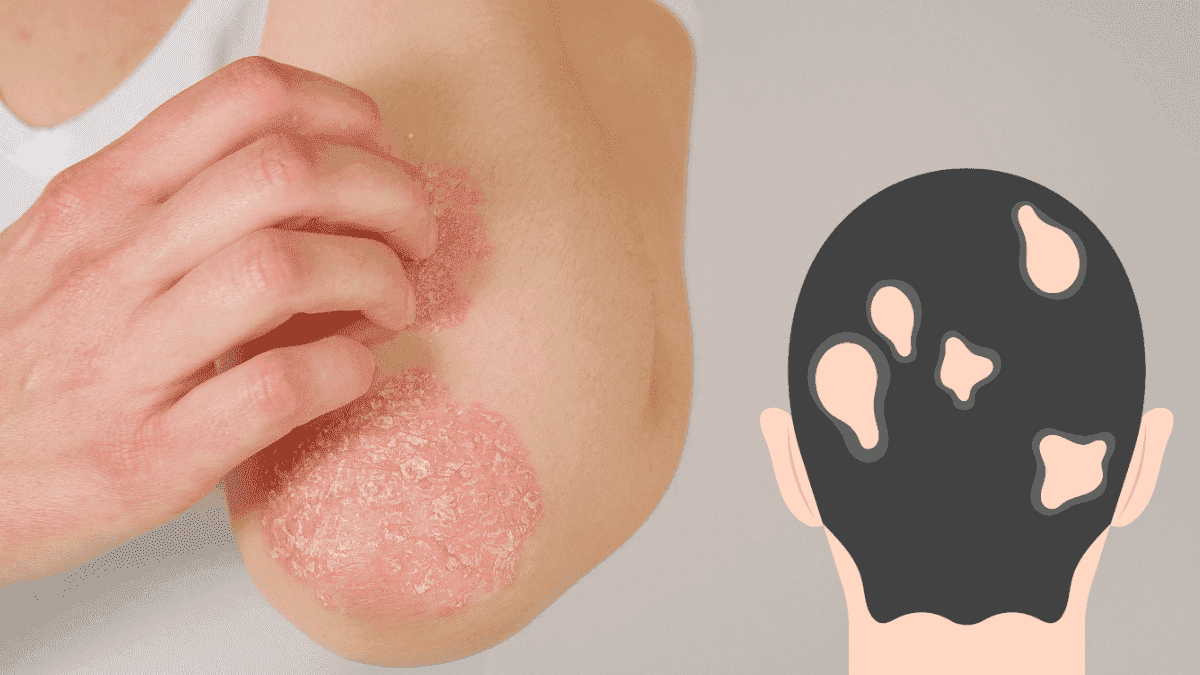
Elbows and Knees: These areas are often affected by skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema, leading to thick, scaly patches. The skin here is naturally thicker and can be more susceptible to dryness and irritation.
Scalp: Scaly patches on the scalp may manifest as dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis, characterized by flaking and itching. These conditions can lead to a buildup of dead skin cells, resulting in visible flakes.
Hands and Feet: The hands and feet are common sites for scaly patches due to conditions like athlete’s foot (a fungal infection) or contact dermatitis, which can result from exposure to irritants or allergens. The skin on the palms and soles may become thickened and scaly.
Face and Neck: Scaly patches can appear on the face and neck as a result of conditions like eczema, which can cause inflammation and irritation in these sensitive areas. Psoriasis may also affect the face, leading to noticeable patches.
Chest and Back: The chest and back can develop scaly patches due to various dermatological issues, including fungal infections or allergic reactions. These areas may be less visible but can still be uncomfortable and irritating.
Causes of Scaly Patches
Dry Skin
Dry skin, also known as xerosis, is one of the most common causes of scaly patches. This condition often arises due to environmental factors such as cold weather, low humidity, and excessive heat, all of which can strip moisture from the skin.
Additionally, frequent exposure to hot showers or baths can damage the skin’s natural oils, leading to increased dryness. As we age, our skin naturally produces less oil, making it more prone to dryness and scaly patches.
Certain skin care products, especially those that are harsh or drying, can also contribute to the problem. Managing dry skin typically involves regular moisturizing, avoiding hot showers, and using gentle cleansers to help retain hydration.
Skin Conditions (e.g., Psoriasis, Eczema)
Various dermatological conditions can result in scaly patches. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to thick, red patches covered with silvery scales.
These patches can often be itchy and painful, commonly appearing on areas like the elbows, knees, and scalp. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is another prevalent condition that causes inflamed, itchy, and dry patches on the skin. This condition can occur anywhere on the body and is especially common in children, although it can persist into adulthood.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects oily areas such as the scalp and face, leading to yellowish, greasy scales and contributing to dandruff. Treatments for these conditions may involve topical medications, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes systemic therapies.
Allergies and Irritants
Allergic reactions and irritants can also lead to scaly patches. Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to substances like soaps, cosmetics, or certain metals such as nickel, resulting in redness, itchiness, and scaling in the affected areas.
Allergic reactions can stem from exposure to allergens, including specific foods, plants (like poison ivy), or medications, leading to dermatitis characterized by scaly patches.
Effective management involves identifying and avoiding known allergens or irritants and using appropriate topical treatments to soothe the skin.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are another potential cause of scaly patches. Conditions like tinea, commonly known as ringworm, can affect various parts of the body, including the scalp, feet, and groin.
This infection typically presents as a red, ring-shaped patch with a scaly border. Seborrheic dermatitis can also result from an overgrowth of yeast on the skin, particularly in oily areas, leading to flaky patches.
Treatment for fungal infections generally involves antifungal medications or topical treatments aimed at reducing fungal growth and alleviating symptoms.
Symptoms Accompanying Scaly Patches
Itching and Irritation
One of the most common symptoms associated with scaly patches is itching. This can range from a mild, occasional itch to intense discomfort that can disrupt daily activities. The itchiness often results from the underlying skin condition that causes the scales, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Scratching the affected area can lead to further irritation and inflammation, exacerbating the problem. In some cases, the skin may feel tender or sensitive, adding to the overall discomfort. Managing the itch is crucial, as scratching can damage the skin and potentially lead to secondary infections.
Redness and Inflammation
Redness and inflammation are often noticeable around scaly patches. This can manifest as pink or red areas surrounding the patches, indicating irritation or an inflammatory response from the skin. In conditions like psoriasis, the skin may not only be red but also feel warm to the touch.
Inflammation can be a sign that the body is reacting to an irritant or a skin condition, and it may be accompanied by swelling in the affected area. Addressing inflammation is important, as persistent redness can lead to further skin damage if left untreated.
Cracking and Peeling
Cracking and peeling are additional symptoms that can occur with scaly patches, particularly in severe cases. As the skin becomes increasingly dry and irritated, it may start to crack, leading to painful fissures that can bleed or become infected.
This symptom is particularly common in areas where the skin is naturally thicker, such as the elbows and knees. Peeling can also occur, resulting in flakes of skin that may be unsightly and uncomfortable. Managing dryness through regular moisturizing and avoiding irritants is essential to prevent cracking and peeling, promoting overall skin health.
Conclusion
Scaly patches on the skin can be a source of discomfort and concern, often indicating underlying issues that require attention. Understanding the causes—whether they stem from dry skin, specific skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema, allergic reactions, or fungal infections—can help in identifying appropriate treatments.
Common symptoms, including itching, redness, inflammation, and cracking, further illustrate the impact these patches can have on your daily life.
If you notice persistent or worsening scaly patches, it’s crucial to seek advice from a healthcare professional. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend tailored treatment options to alleviate symptoms and restore your skin’s health.
FAQs
What causes scaly patches on the skin?
Scaly patches can be caused by dry skin, skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema, allergies, and fungal infections.
Are scaly patches itchy?
Yes, scaly patches often cause itching and irritation.
How can I treat scaly patches?
Treatment may include moisturizers, topical medications, and lifestyle changes, depending on the underlying cause.
When should I see a doctor for scaly patches?
You should consult a doctor if the patches are persistent, worsening, or accompanied by severe symptoms.
Can scaly patches be prevented?
Yes, maintaining proper skincare, avoiding known irritants, and staying hydrated can help prevent scaly patches.