Understanding Eye Diseases
What Are Eye Diseases?
Eye diseases refer to a broad spectrum of conditions that can affect various parts of the eye, leading to changes in vision and overall eye health. These diseases can stem from numerous factors, including genetic predispositions, age-related changes, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices.
Awareness of eye diseases is vital, as early detection can facilitate effective treatment and prevention strategies, ultimately helping individuals maintain their vision and improve their quality of life.
Common Types of Eye Diseases
Cataracts are among the most common eye diseases, characterized by the clouding of the eye’s lens, which can cause blurred vision and increased sensitivity to light. Glaucoma, another prevalent condition, involves increased pressure within the eye, potentially leading to optic nerve damage and peripheral vision loss if left untreated.
Macular degeneration primarily affects the central part of the retina, causing distortion or loss of central vision, especially in older adults. Diabetic retinopathy arises as a complication of diabetes, resulting in damage to the retinal blood vessels and symptoms like blurred vision.
Lastly, conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, often caused by infections or allergies, leading to redness and discomfort. Understanding these common eye diseases can empower individuals to recognize symptoms and seek timely care, ensuring better eye health.
Symptoms of Eye Diseases
Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the early warning signs of eye diseases is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. Common early symptoms may include subtle changes in vision, such as difficulty focusing or occasional blurriness. Some individuals might experience increased sensitivity to light or difficulty adjusting from bright to dim environments.
Additionally, frequent headaches or eye strain can signal underlying issues. Other warning signs include the appearance of floaters or flashes of light, which can indicate changes in the vitreous gel of the eye.
Being vigilant about these symptoms can help individuals seek appropriate care before conditions worsen.
Severe Symptoms to Watch For
Severe symptoms often indicate that an eye condition has progressed and requires immediate attention. Sudden vision loss, whether partial or complete, is a critical warning sign that necessitates urgent evaluation.
Other severe symptoms include persistent eye pain, redness accompanied by swelling, or the presence of discharge that may suggest infection. If individuals experience halos around lights or a sudden increase in floaters, these could signify serious conditions like retinal detachment or glaucoma.
Promptly addressing these severe symptoms is essential to prevent further complications and protect vision.
Diagnosis of Eye Diseases
Common Diagnostic Tests
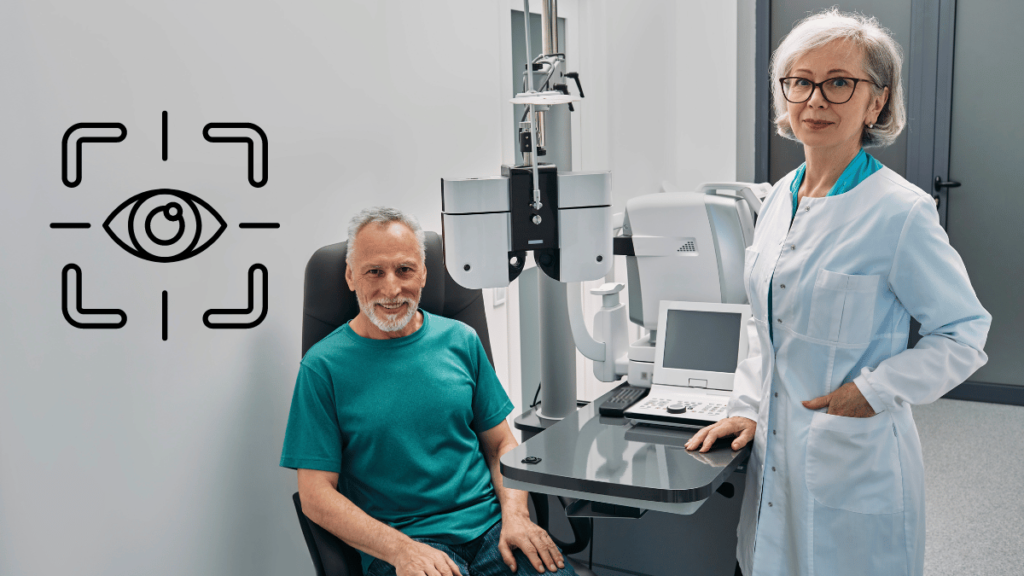

Diagnosing eye diseases involves a variety of tests designed to assess vision and the health of the eyes. A comprehensive eye exam typically includes visual acuity tests,
which measure how well a person can see at various distances. Tonometry is another crucial test that measures intraocular pressure, helping to detect conditions like glaucoma.
Ophthalmoscopy allows the eye care professional to examine the retina and optic nerve for signs of disease. Additionally, visual field tests evaluate peripheral vision, while imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) provide detailed images of the eye’s structures.
These diagnostic tests are essential for identifying eye diseases early and determining appropriate treatment plans.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are vital for maintaining eye health and preventing vision loss. These exams enable early detection of potential eye diseases, often before symptoms appear. Individuals at higher risk—such as those with a family history of eye conditions, diabetes, or other systemic health issues—should have more frequent check-ups.
Routine exams not only help monitor existing conditions but also assess overall eye health, ensuring that any changes are promptly addressed. By prioritizing regular eye exams, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their vision and overall well-being.
Treatments for Eye Diseases
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for eye diseases vary depending on the specific condition but often include medications aimed at managing symptoms and preventing progression. For instance, eye drops are commonly prescribed for conditions like glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure.
Anti-inflammatory medications may be used to treat conditions such as uveitis, while antibiotic or antiviral medications can address infections like conjunctivitis. Additionally, regular monitoring and management of systemic conditions, such as diabetes, are crucial for preventing complications related to diabetic retinopathy.
These medical interventions are essential for maintaining eye health and preventing further deterioration.
Surgical Options
In some cases, surgical options may be necessary to effectively treat eye diseases. Cataract surgery, one of the most common procedures, involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial one to restore clear vision.
For glaucoma, procedures such as trabeculectomy or laser therapy can help lower eye pressure and protect the optic nerve. Retinal surgeries, including vitrectomy, may be performed to address conditions like retinal detachment or severe diabetic retinopathy.
While surgery carries its own risks, these procedures can significantly improve vision and quality of life for many individuals suffering from serious eye conditions.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, home remedies and lifestyle changes can play a supportive role in managing eye health. Simple practices such as maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can promote good vision.
Regular exercise and staying hydrated also contribute to overall eye health. Additionally, protecting the eyes from harmful UV rays by wearing sunglasses and reducing screen time can help prevent strain and damage. Incorporating regular breaks during screen use—following the 20-20-20 rule—can alleviate digital eye strain.
These holistic approaches, combined with professional treatments, can enhance eye health and well-being.
Prevention of Eye Diseases
Healthy Habits for Eye Health

Adopting healthy habits is essential for maintaining optimal eye health and preventing eye diseases. Regular eye examinations allow for early detection of potential issues, even before symptoms arise.
Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as avoiding touching the eyes with unwashed hands and properly cleaning contact lenses, can reduce the risk of infections. Engaging in regular physical activity not only improves overall health but also promotes good circulation, benefiting eye function.
Furthermore, managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, is crucial, as these can significantly impact eye health if left unchecked.
Importance of Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in preserving eye health and preventing disease. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports optimal eye function.
Foods high in vitamins A, C, and E, along with zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce the risk of age-related eye diseases such as macular degeneration and cataracts.
Incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, leafy greens, and fatty fish into your diet can provide the necessary nutrients for healthy eyes. Staying hydrated is equally important, as proper hydration helps maintain optimal eye moisture and function.
Protecting Your Eyes from UV Rays
Protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays is crucial for preventing eye damage and diseases, such as cataracts and macular degeneration. Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays is an effective way to shield your eyes when outdoors. Additionally, wearing a wide-brimmed hat can provide extra protection.
It’s also important to be cautious about prolonged exposure to bright screens and glare, as this can contribute to eye strain. Using blue light filters on devices and practicing the 20-20-20 rule—taking a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away every 20 minutes—can help alleviate digital eye strain.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding eye diseases and their prevention is essential for maintaining good vision and overall eye health. Recognizing early warning signs and seeking timely diagnosis through regular eye exams can significantly improve outcomes.
Various treatment options, including medical therapies, surgical interventions, and supportive home remedies, play crucial roles in managing eye conditions effectively.
Moreover, adopting healthy habits, prioritizing nutrition, and protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays can greatly reduce the risk of developing serious eye diseases. By taking proactive steps and making informed choices about eye care, individuals can preserve their vision and enhance their quality of life.
FAQ about Eye Diseases
What are the common symptoms of eye diseases?
Common symptoms include blurred vision, eye pain, redness, and sudden vision loss.
How often should I have an eye exam?
It’s recommended to have an eye exam every one to two years, depending on your age and risk factors.
Can eye diseases be prevented?
Many eye diseases can be prevented through regular eye exams, healthy habits, and proper nutrition.
What is the most common eye disease?
Cataracts are the most common eye disease affecting older adults.
Are there home remedies for eye health?
Yes, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and taking regular breaks from screens can support eye health.